Table of Content
- Data API Documentation
Below you will find the API Documentation.
Data API Documentation
The installed request handler will expose a well-defined API to the consumers of the application for transferring and manipulating data of the exposed business domain objects (BDO).
There are two implementations as Open Source available on Github which are supporting this specfication
- Google AppEngine based implementation which can be found in clb-appEngineBackend
- NodeJS based implementation which can be found in clb-modelLoader
There are minor differences in the two implementation which will be listed in the documentation.
Format and Protocol
REST API which is supporting the JSON format via the HTTP protocol.
Base URL
All URLs referenced have the following format:
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId>
Subresources
The model loader will create for each defined a model a subresource which will be make up the next level of the overall URL.
HTTP GET
The following GET operations are supported
Returning a list of objects
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId>/<collection>/`
For example the above defined moongoose customers collection URL would look like:

Pagination
The current implementation will return partial response only limiting to 20 records, which can be paged through. This limit will be made configurable in an upcoming release.
Due to the fact that I’m using this inteface for two backendstyles
- Mongo Database Backend
- Google AppEngine Backend
I support to styles of pagination
maxRec/limit/offsetstylecursorstyle
maxRec/limit/offset style (MongoDB)
By default the last JSON record entry will contain additional technical and meta information about the request, necessary for allowing consumers to implement a paging.
{
_maxRec: "3",
_limit: "20",
_offset: "0"
}
_maxRecwill list the total amount of records in the collection_limitwill list the maximum number of requests which are given back_offsetwill tell you which set of records was passed back, i.e. an_offsetof200would mean that result list skipped the first 199 records and presents the records from200-220
Pagination Control Parameters
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId</<collection>?offset=<number>
Use offset to skip a number of records, as for example with a limit of 20, you would send a first request with offset=0 then offset=20, then offset=40 etc. until you reached _maxRec.
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId</<collection>?maxRec=<number>
By passing in a maxRec parameter (normally the one gotten by an earlier paging requerst), the request handler will by pass the database count objects statement, which results in one db activity less (performance optimization). The passed in number will passed back via _maxRec entry. Normally a consumer will fetch in the first request the _maxRec number and pass it back for the subsequent request, resulting in a faster data access request.
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId</<collection>?limit=<number>
Use limitthe restrict the number of records returned. The number must be less than the maximal limit number allowed (currently 20).
cursor style (Google AppEngine)
Also here the last JSON record entry will contain additional meta information about the request, allowing for paging. It’s the so-called cursor an opaque identifier.
{
_cursor: "E-ABAIICLGoTY3J5cHRpYy1lcGlzb2RlLTM1NnIVCxIIQ3VzdG9tZXIYgICAgICA6goMFA"
}
In the Google AppEngine Backend counting of objects is always inefficient and therefore the cursor style paging is supported. The returend opaque identifier has to be provided as additional query parameter for the subsequent call
Pagination Control Parameters
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId</<collection>?cursor=<number>
This allows you to page to arbitrary large collections.
Partial Response
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId</<collection>?fields=<field1>,<field2>
Allows you to return only a partial response by listing the fields you are interested in. By default the _id field will be always included.
Request Sample
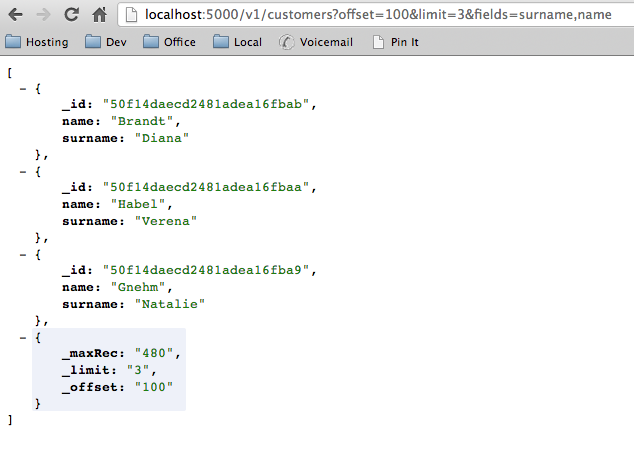
Filtered Result Set
It’s possible to filter the result set
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId</<collection>?fiter=<fieldName1>:<value1>,<fieldName2>:<value2>,_options:<value>
With the following conventions:
- Multiple
<fieldName>:<value>pairs will be joined with and logicalAND - The special fieldName
_optionswill be used to provide additional options. Currently there is only one option definedlikeby defaulf the filter will trigger an exact search, by usinglikea pattern search will be triggered, which is filtering a value with containes the passed in filter value.- In case of the Google AppEngine implementation the
likequery will filter entries which start with the relevant filter name (not a full like). BigTable, which is the database back end for App Engine, will scale to millions of records. Due to this, App Engine will not allow you to do any query that will result in a table scan, as performance would be dreadful for a well populated table
Returning a dedicated object
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId>/<collection>/<id>`
Will return the object with the corresponding id.
In case the object doesn’t exist an empty response will be returned.
{}
Partial Response
Applies according to the definition as described above in the get list of objects.
Returning a set of dedicated objects
In case you want to return a set of objects use set request parameter and provide the corresponding identifiers as a comma separated list
http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<versionId>/<collection>?set=<id1>,<id2>,<id3>`
Will return the object with the corresponding id.
Partial Response
Applies according to the definition as described above in the get list of objects.
HTTP PUT
`http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<url>/<versionId>/<collection>/<id>`
Changes the attributes of the object associated with the corresponding id. As a reply the updated object will be passed back as a JSON record.
HTTP POST
`http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<url>/<versionId>/<collection>/`
Creates the object which is passed in. As a reply the the created object will be passed back as a JSON record (including the newly created _id will be passed back.)
HTTP DELETE
`http(s)://<yourDomainName>/<url>/<versionId>/<collection>/<id>`
Will delete the corresponding object. As a succesful result the status code 200 will be returned.
Status/Error Handling
HTTP Status Code 200 - OK
Will be returned for a succesful action (e.g. new object creation)
HTTP Status Code 400 - Bad Request
Will be returned in case the request sent by the consumer was not correct (e.g. wrong parameters)
HTTP Status Code 404 - Not Found
The resource was not found. There is nothing on that endpoint URI. The returned JSON is empty.
`{}`
HTTP Status Code 500 - Int. Server Error
Will be returned in case there is a error in the technical server infrastructure.
Error Return Structure
In case of an error the following JSON Error structure will be given back together with above defined HTTP Status code.
{
"message":"Bad Request Query Parameter provided to the clb-modelloader API for \"customers\": \"limit\" parameter is number",
"errorCode":"0001",
"moreInfo":"http:api.cloudburo.com/errors/0001"
}
Date/Timestamp Handling
Any date and timestamp returned by the REST API Layer will follow the rule of the ISO8601 standard. It will be of the following format:
yyyy-MM-dd'T'HH:mm:ss.SSSXXX
As for example
birthdate: "1964-02-21T00:00:00.000+01:00"